
The hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) market has grown due to increased consumer demand, fuel efficiency improvements, environmental impact, and stricter vehicle emission policies worldwide. There are several different HEV architectures. The different architecture types, referred to as P0-P4, depend on the way the electric drive is connected to the powertrain system via a belt, integrated or mesh.
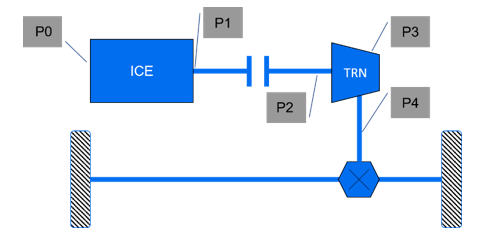
Diagram 1: Illustrates the connection points in a typical powertrain for an electric machine.
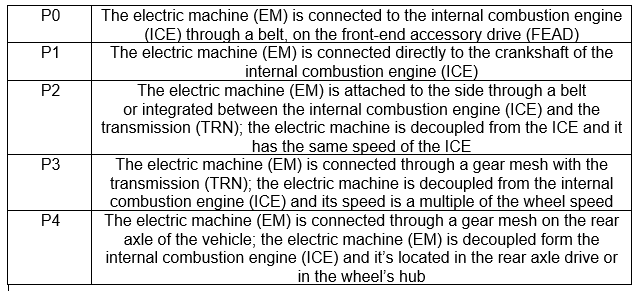
Chart 1: Explains the four different HEV architectures, P0-P4.
One of the most popular architectures is the P0 configuration-based hybrids because it is the most cost effective due to the limited impact of the 48V system on the existing vehicle design. In a P0 HEV architecture, the electric drive is connected to the internal combustion engine by a belt on the front-end accessory drive (FEAD). The popularity of implementing a P0 HEV architecture into an existing vehicle design increased because of ease of integration. However, the integration does not come without some engineering challenges.
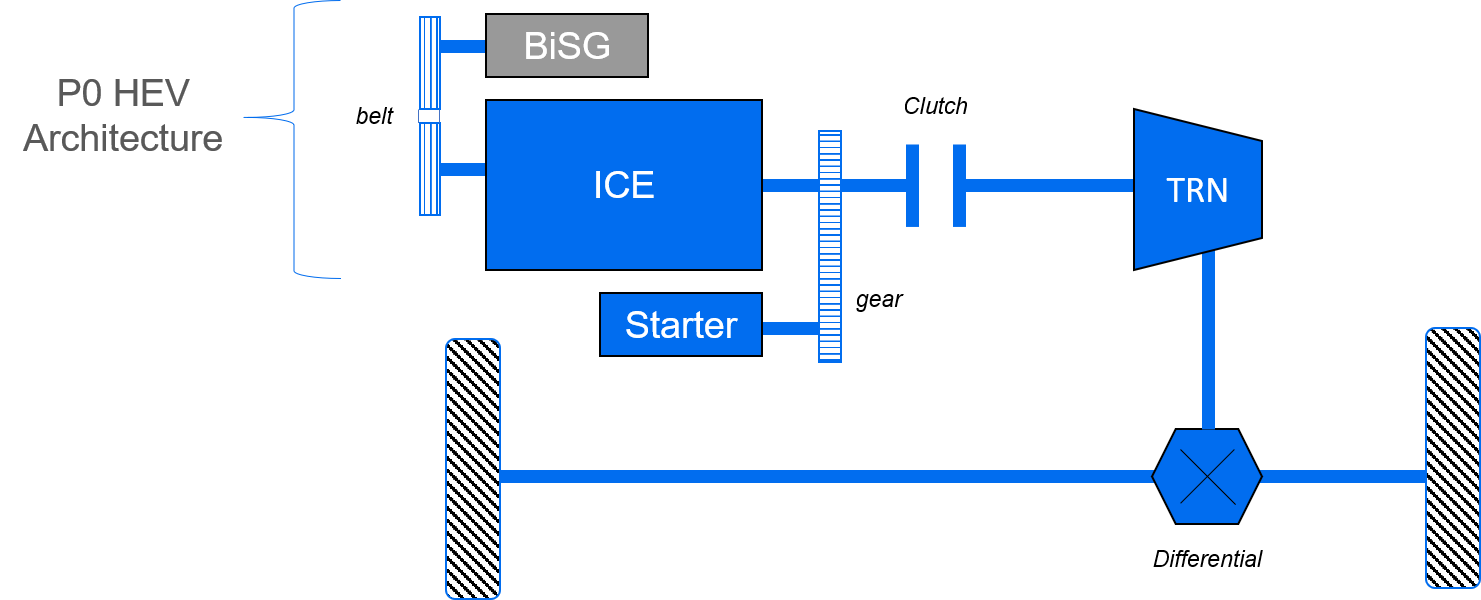
Diagram 2 – Illustrates the HEV P0 architecture, where the electric machine or the BiSG is connected to the internal combustion engine (ICE) through a belt, on the front-end accessory drive (FEAD).
Recently, Ball Systems was chosen to become an extension of our customer’s team to facilitate the completion of six durability test stations. The customer’s engineering team developed a new motor generator for P0 HEVs and needed to have accelerated lifecycle testers designed and built. The motor generators being tested are a new technology family for this supplier and created multiple new technology challenges for them.
Check out our latest case study to learn more about how our team is breaking down barriers with new test station technology in the HEV industry.

Blog Comments